Single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes encoding xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes are associated with predisposition to arterial hypertension
Aннотация
Background: Arterial hypertension (AH) is the most common disease of the cardiovascular system. Intracellular chemical and oxidative stress, which can be associated both with direct exposure to toxic xenobiotics and with their excessive activation during biotransformation, may lead to endothelial dysfunction and increased risk of AH development. The aim of the study: To investigate the association of single nucleotide polymorphisms of genes involved in the biotransformation of xenobiotics (rs1048943 CYP1A1, rs762551 CYP1A2, rs1056836 CYP1B1, rs1799930 NAT2, rs1800566 NQO1, rs11045642 MDR1) with predisposition to arterial hypertension. Materials and methods: A total of 702 patients with AH (307 men, 395 women; mean age 55 years) and 857 gender- and age- matched relatively healthy volunteers (406 men, 451 women; mean age 53 years) were recruited for the study. Genotyping of SNPs were done using TaqMan-based PCR. Results: Comparative analysis of genotype frequencies (log-additive regression model was used, all calculations were performed with adjustment for gender, age) showed that SNP rs762551 CYP1A2 was associated with a decreased risk of AH (ORadj=0.85, 95%CIadj=0.73-0.99; Padj=0.038); SNP rs1045642 MDR1 (ABCB1) was associated with an increased risk of AH (ORadj=1.20, 95% CIadj=1.04-1.39; Padj=0.013). Moreover, SNP rs762551 CYP1A2 was associated with the age of manifestation of arterial hypertension (Differenceadj=1.51; 95%CIadj=0.22-2.80) and cholesterol level (Differenceadj= -0.15; 95% Cladj = -0.29 - -0.01). Conclusion: Thus, in this study, for the first time, there was found the association of rs762551 CYP1A2 and rs1045642 ABCB1 (MDR1) with arterial hypertension in Russians.
Ключевые слова: arterial hypertension, cytochrome P450, biotransformation of xenobiotics, rs762551, CYP1A2, rs1045642, MDR1, ABCB1
К сожалению, текст статьи доступен только на Английском
Introduction. Arterial hypertension (AH) is the most common disease of the cardiovascular system. More than 30% of the world's adult population suffer from AH [1]. From a genetic point of view, AH is a multifactorial polygenic hereditary disease.
Numerous studies prove that various aerosol polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are the main source of organic toxic chemicals with potential effects on the cardiovascular system [2]. PAHs are widely spread in the environment: they are found in cigarette smoke, they are formed during cooking with incomplete combustion of organic materials such as coal and oil products, they are by-products of various industrial enterprises [3]. Intracellular chemical and oxidative stress, which can be associated both with direct exposure to toxic xenobiotics and with their excessive activation during biotransformation, are the cause of endothelial dysfunction. In particular, it was shown that nitrated and oxidized polyaromatic hydrocarbons can reduce both the activity of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) and NO production through mechanisms associated with the effect of phosphorylated eNOS on eNOS mRNA expression and eNOS protein expression [4]. Considering the crucial role of NO in the regulation of vascular tone and endothelial dysfunction [5], it is obvious that variations in genes involved in different stages of biotransformation of xenobiotics can be a risk factor for the development of arterial hypertension through participation in key pathogenetic mechanisms of AH development.
Cytochrome P4501A1 (CYP1A1) is an important member of the CYP family and is responsible for the metabolism of a large number of xenobiotics, as well as some endogenous substrates. In particular, CYP1A1 acts as a major enzyme in the metabolism of PAHs [6]. CYP1A1 is also involved in the production of vasoactive substances based on arachidonic acid – epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE), which are endogenous defense mechanisms against cardiovascular disease [7]. Moreover, CYP1A1 is also involved in the oxidative metabolism of estradiol and estrone [8]. The rs1048943 CYP1A1 genetic variant is one of the most functionally significant. Substitution of A for G in the 7th exon of the gene leads to the replacement of Isoleucine with Valine in the structure of the enzyme (Ile462Val). This SNP is located in the heme-binding region of the protein CYP1A1 and can lead to a twofold increase in enzyme activity [9].
CYP1A2 encoded by the CYP1A2 gene, participates in the metabolism of a wide range of xenobiotics, such as heterocyclic aromatic amines and PAHs [10]. CYP1A2 is also an important enzyme, which is responsible for the metabolism of caffeine. CYP1A2 expression is induced by environmental chemicals and is highly variable between individuals [11]. CYP1A2 gene is highly polymorphic. The rs762551 CYP1A2 genetic variant can lead to a 2-3-fold increase in protein activity [12].
CYP1B1 – cytochrome P450 product – oxidizes various compounds such as steroids (17-beta-estradiol), fatty acids, retinoids and xenobiotics including PAHs. In blood vessels, CYP1B1 is expressed predominantly in vascular smooth muscle cells, to a lesser extent – in endothelial cells [13]. In animal experiments, it was shown that the endothelial dysfunction observed in angiotensin II-induced hypertension in mice was prevented by silencing the CYP1B1 gene [14]. The most studied rs1056836 genetic variant in the CYP1B1 gene leads to the replacement of Leucine with Valine at the 432 position of the encoded protein [15].
NAT2 is a phase II xenobiotic biotransformation enzyme which carries out conjugation of exogenous arylamine-containing substances, components of some drugs, caffeine [16]. The gene encoding cytosolic N-acetyltransferase is located on chromosome 8p22. Variations in the NАТ2 gene lead to a change in the level of functional activity of isoniazid acetylation, which has been classified as fast, intermediate, and slow [17]. Amino acid replacement 590G>А (Arg>Gln; rs1799930) leads to a change in the functional activity of the enzyme. Slow acetylation phenotype associated with the АА NAT2 genotype is unable to conjugate to metabolites or toxins; GA heterozygotes have intermediate enzyme activity.
NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) – an enzyme of phase II of biotransformation of xenobiotics – catalyses the reduction of various quinones using NAD (P) H as an electron donor. The transformation of quinones to hydroquinones using NQO1 represents an important mechanism of cell defence against oxidative and chemical stress [18]. Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs1800566 NQO1 in the 6th exon of the gene leads to the substitution of Proline for Serine in the 187th amino acid. It was shown that the 187SS variant genotype causes a complete loss of the enzymatic activity of NQO1, while in heterozygotes 187PS there is an almost threefold decrease in the enzyme activity.
The multidrug resistance gene (MDR1) encodes an integrated transmembrane protein, P-glycoprotein, which plays an important role in the bioavailability of certain drugs, as well as in the protection of cells from toxic substances and metabolites through the action of an ATP-dependent mechanism of "cell outflow" [19]. MDR1 has broad substrate specificity. Of more than 50 single nucleotide polymorphisms of MDR1, the functionally significant C3435T (rs1045642) is the most widely studied [20].
The aim of the study was to investigate the association between common SNP in genes encoding xenobiotics biotransformation enzymes (rs1048943 CYP1A1, rs762551 CYP1A2, rs1056836 CYP1B1, rs1799930 NAT2, rs1800566 NQO1, rs1045642 MDR1) and the risk of AH.
Materials and methods. A total of 1559 unrelated Russian individuals from the Kursk region were examined; written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to entering the study. This study included 702 patients with diagnosis of arterial hypertension. AH patients were hospitalized in the cardiac units of the Kursk Regional Clinical Hospital and the Kursk City Clinical Emergency Hospital in the period 2011-2017 [21, 22, 23]. The AH group included patients with systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mm Hg. and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP)≥90 mm Hg, as well as patients who received antihypertensive therapy. Exclusion criteria: symptomatic arterial hypertension, acute inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, severe kidney or liver disease, oncological pathology, pregnancy. Patients with ischemic heart disease, cerebral stroke, diabetes mellitus were also excluded from the study. The control group consisted of 857 gender- and age-matched healthy individuals, without a history of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and with normal level of blood pressure (Table 1). The control group was formed from relatively healthy volunteers, as well as during professional examinations at industrial enterprises, in medical institutions of Kursk and the Kursk region. The formation of AH group and control group was carried out using a continuous method.
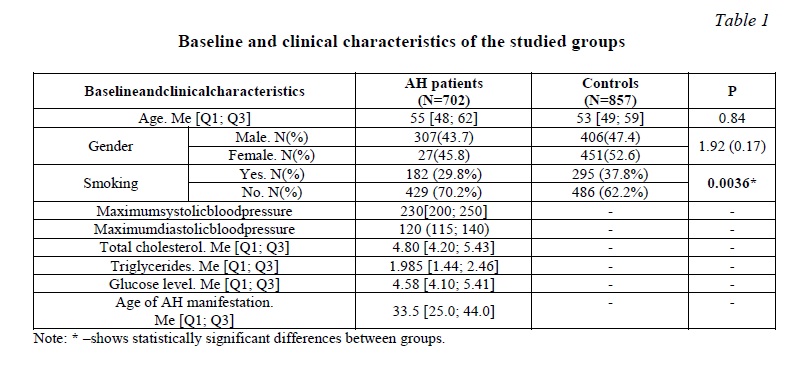
The study was approved by the Regional Ethics Committee of Kursk State Medical University. All patients signed a voluntary informed consent to participate in the study. Venous blood samples were obtained from all individuals. Genomic DNA was isolated from peripheral blood using the standard phenol-chloroform extraction procedure. The main criteria for SNP selection were the functional significance of polymorphism and the frequency of the minor allele over 5%. Genotyping of rs1048943 CYP1A1, rs762551 CYP1A2, rs1056836 CYP1B1, rs1799930 NAT2, rs1800566 NQO1, rs1045642 MDR1 was performed by TaqMan-based PCR using CFX96 detection system (Bio-Rad, USA). Regenotyping of 10% of the studied samples, selected on a random basis and in the absence of information about the status of the disease, showed 100% reproducibility of the original results.
To assess the associations of genotypes with predisposition to AH, the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI), calculated for the log-additive regression model, were used. All calculations were performed with corrections for gender and age in the SNPStats program available online (https://www.snpstats.net/start.htm). To assess the regulatory potential of SNPs, bioinformatic resources available online were used: QTLbase (http://mulinlab.org/qtlbase) and HaploReg v.4 (https://pubs.broadinstitute.org/mammals/haploreg/haploreg.php).
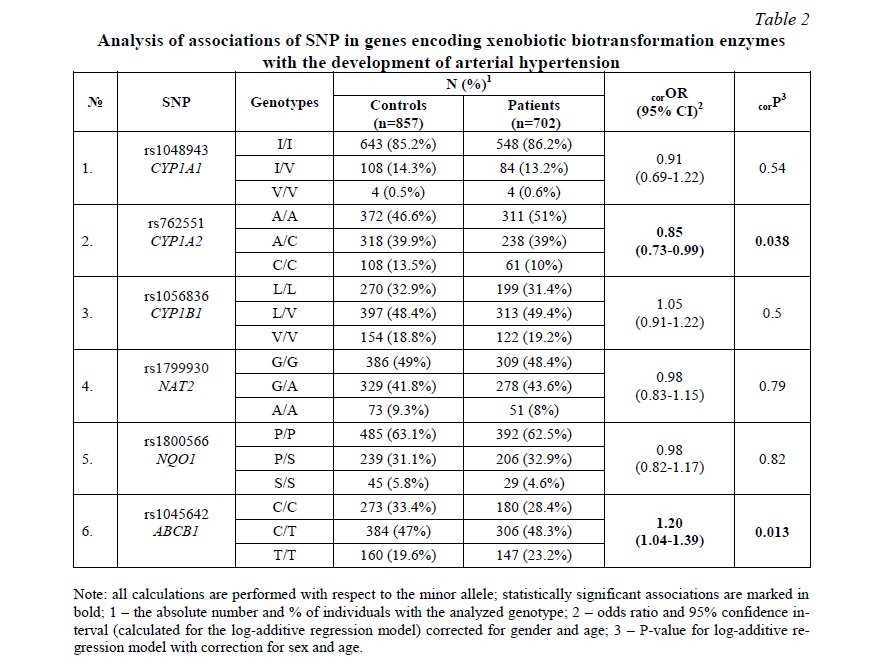
Results and discussion. The analysis of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was carried out in the control group. The distribution of genotype frequencies for all studied SNPs, except for rs762551 CYP1A2, corresponded to the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (P> 0.05). For rs762551 CYP1A2, we revealed a decrease in observed heterozygosity (0.40) versus expected (0.45); P <0.01.
SNP rs762551 CYP1A2 was associated with a decreased risk of AH (OR=0.85, 95% CI=0.73-0.99, P=0.038). SNP rs1045642 ABCB1 was associated with an increased risk of AH (OR=1.20, 95% CI=1.04-1.39, P=0.013) (Table 2).
Subsequent analysis of the relationship of the studied genetic variants with clinical and laboratory parameters in patients with AH revealed an association of rs762551 CYP1A2 with the age of manifestation of AH and cholesterol level: carriers of the C/C genotype had the lowest cholesterol levels and the latest manifestation of hypertension (Table 3). It should also be noted that SNP rs1799930 NAT2 was associated with blood glucose levels.
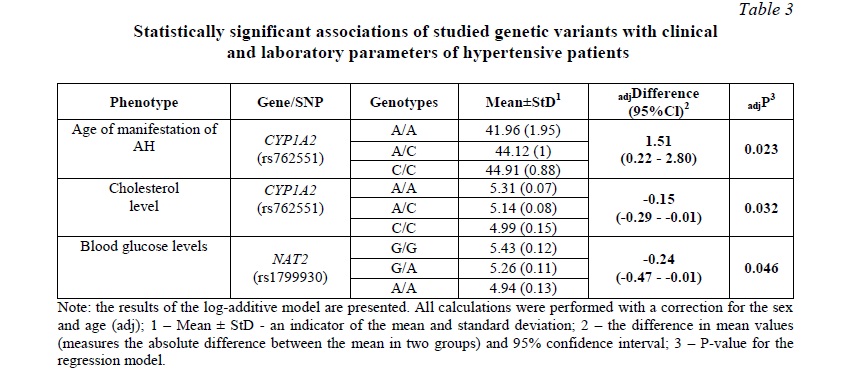
Our study revealed an association of rs762551 CYP1A2 with the decreased risk of AH. This association was discovered for the first time in the population of Central Russia. It is important that rs762551 CYP1A2 was associated with age at onset of AH and cholesterol levels. The CYP1A2 gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. Cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases that catalyse reactions involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics and the synthesis of sex steroids, cholesterol, and other lipids. The protein encoded by this gene is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum, and its expression is induced by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), some of which are found in components of cigarette smoke. The endogenous substrate of the enzyme is unknown; however, it is able to metabolize some PAHs to intermediates (https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=CYP1A2). Previous studies have already shown an association of rs762551 polymorphism with blood pressure variability and hypertension [24]. It is known that the studied rs762551 CYP1A2 is in linkage disequilibrium with the SNP rs1378942 (HapMap CEU), which is located in the CYP1A2 gene cluster and showed the strongest association with diastolic blood pressure in Europeans [25]. Moreover, an association between rs762551 and the risk of AH was shown in the study by Guessous I, et al [26], who noted a negative association of rs762551 with hypertension in non-smokers, modified by caffeine intake. The previous studies of CYP1A2 in mice have demonstrated an important role for this enzyme in oxidative stress [27] and in lipid metabolism [28], which could explain the effect of the rs762551 CYP1A2 on cholesterol levels found in our study. It was shown that CYP1A2 -/- mice were characterized by a change in the expression of genes involved in the pathways of cholesterol biosynthesis and fatty acid metabolism. Moreover, in patients with cardiovascular diseases, which were characterized by low CYP1A2 activity, there was an increased level of inflammatory cytokines that may be involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases [29]. These observations indicate that low CYP1A2 levels have adverse biological effects that may explain not only the increased risk of AH, but also impaired cholesterol metabolism.
Bioinformatics analysis was performed to explain the functional effects of rs762551 CYP1A2. According to the QTLbase, the carriage of the protective C allele is associated with 17 cis-mQTLs associated with a decrease in methylation of CpG sites in CYP1A2 (Table 4). Because a decrease in methylation can lead to an increase in gene expression, the protective effects of the C allele can also be mediated by cis-mQTL. At the same time, for the risk allele A, 2 cis-hQTLs were found associated with a decrease in acetylation at the 27th lysine residue on the histone H3 protein in CD14+ monocytes and CD16+ neutrophils in peripheral blood and, therefore, with a potential decrease in CYP1A2 expression (Table 4).
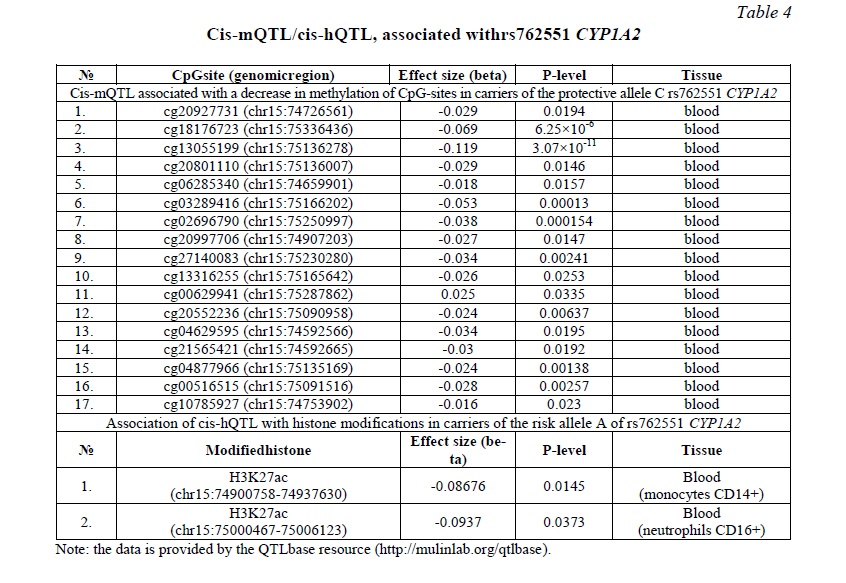
According to the HaploReg database (v4.1), this polymorphism is associated with trans-eQTLs for the ULK3 gene in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue, pancreas, whole blood (ULK3 encodes serine/threonine kinase protein, which acts as a regulator of autophagy); for the CSK gene in whole blood (tyrosine protein kinase CSK; non-receptor tyrosine protein kinases, which play an important role in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, migration, immune response) (https://pubs.broadinstitute.org/mammals/haploreg/detail_v4.1.php ? query = & id = rs762551). Therefore, rs762551-trans-eQTLs may be associated with the development of AH through mechanisms involved in the regulation of growth, differentiation, cell migration, and autophagy processes.
Thus, the present study provided additional evidence that CYP1A2 is an important gene for cardiovascular diseases susceptibility.
Another gene involved in xenobiotics biotransformation and associated with AH was MDR1 (multidrug resistance gene). It was found that the genetic variant 3435C> T (rs1045642) ABCB1 (MDR1) was associated with an increased risk of AH. P-glycoprotein, a protein from the ABCB-transporter family, is involved in the active transport of xenobiotics from the intracellular to the extracellular space [30]. This trans-membrane protein is expressed in numerous tissues, including the vascular endothelial cells. P-glycoprotein is encoded by the ABCB1 gene. The ABCB1 gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 7 and consists of 29 exons (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/5243). Many single nucleotide polymorphisms have been found in this gene; however, the most studied genetic variant is rs1045642. Variation of C3435T in exon 26 does not lead to an amino acid substitution, however, it affects gene expression, in particular, it reduces the stability of mRNA and, as a consequence, the activity of the transmembrane P-glycoprotein [31]. In a study of the Chinese Han population, rs1045642 ABCB1 has been shown to be associated with blood pressure [32]. It was also found that this SNP is associated with an increased risk of AH in patients with chronic kidney disease [33].
The association of C3435T ABCB1 with AH can be explained by three mechanisms. Firstly, it is known that P-glycoprotein is involved in the secretion of aldosterone in the adrenal glomerular zone [34]. Secondly, animal studies have shown that P-glycoprotein is involved in the transport of oxidized glutathione and thus is associated with oxidative stress – one of the main triggers of AH [35]. Thirdly, P-glycoprotein significantly affects endothelium-dependent vasodilation, reducing NO synthesis [36].
Protective allele C rs1045642 ABCB1 may be associated with the increased gene expression in blood cells by cis-eQTL-mediated mechanisms (Table 5).

According to HaploReg resource data (v4.1), rs1045642 ABCB1 is located in the region of DNA binding with modified histone H3K27ac marking enhancers (in peripheral blood cells), with modified histone H3K9ac marking promoters (in primary mononuclear cells of peripheral blood).
N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) is phase II xenobiotics biotransformation enzyme which plays an important role in both detoxification and activation of many xenobiotics [16]. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the diseases whose association has been studied in relation to acetylation phenotypes. Previous studies have already shown a positive association between air pollutants and insulin resistance in subjects with the GG genotype of the rapid acetylator phenotype rs1799930 NAT2 [37]. Another study also showed that T2DM patients with the rapid acetylator phenotype (carriers of the GG genotype) had significantly higher absolute insulin levels and lower insulin sensitivity compared with patients characterized by a slow acetylator phenotype [38].
Thus, despite the fact that there were no patients with diabetes mellitus among patients with AH, it can be assumed that the genetically determined type of acetylator by the single nucleotide polymorphism rs1799930 NAT2 can modify the complex of quantitative phenotypic manifestations associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion. Thus, in this study, for the first time, the association of rs762551 CYP1A2 and rs1045642 ABCB1 (MDR1) with AH in the Russians was found, which provides additional evidence for the role of «chemical stress» in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular pathology. It is also worth noting that bioinformatics analysis revealed a high regulatory potential of rs762551 and rs1045642, suggesting a potentially important role of epigenetic mechanisms in the regulation of gene expression. From a practical point of view, the results obtained can be used to develop new approaches to the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, based on the “fight” against toxic xenobiotics of the environment.
Благодарности
I would like to expresses my gratitude to my colleagues, Professor V.P. Ivanov, as well as Professor A.V. Polonikov for valuable suggestions in carrying out this research.





















Список литературы
Список использованной литературы появится позже.